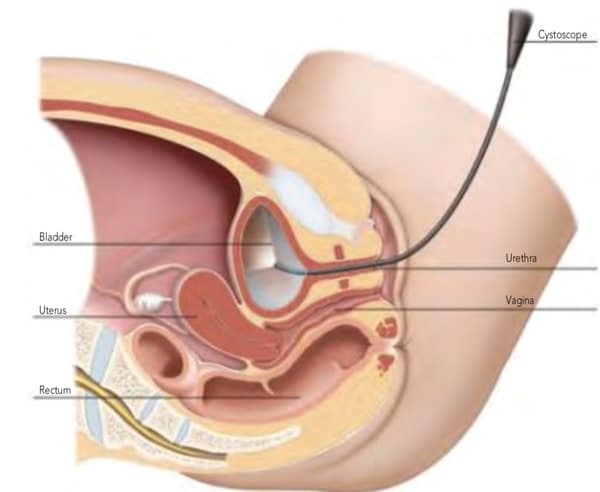
Cystoscopy also is used in the following situations
- Loss of bladder control (incontinence) or overactive blad-der.
- Frequent bladder infections.
- Blood in the urine (hematuria).
- Unusual cells found in a urine sample.
- Pain in the bladder, urethra or during urination.
- During a surgical procedure such as a hysterectomy orincontinence tape procedure, to ensure there has been no damage to the bladder or the ureters.The examination is more successful than other tests, like urine tests or ultrasound, in picking up problems such as bladder stones, bleeding, tumors, and structural abnormalities of the bladder.
The symptoms of endometriosis are related to the areas where endometriosis invades. Endometriosis of the uterosacral ligaments/cul-de-sac leads to painful intercourse, constipation, diarrhea and painful defecation. Endometriosis on the ovary can lead to left sided or right sided pain. Bladder endometriosis may lead to urinary frequency or urgency. You may have only one of the above symptoms or many. Even one symptom can be suggestive of Endometriosis.
Some women have no symptoms yet suffer from infertility. And many women do not have any symptoms, but discover they have endometriosis when are having trouble conceiving. If your doctor told you that you have ‘unexplained infertility’, endometriosis is the culprit in 40-50% of cases of unexplained infertility. If you need an endometriosis specialist in Fort Myers, Naples or Cape Coral, make an appointment with Dr. Bloy. His excision and medical treatment of endometriosis decreases inflammation, pain and will improve fertility.
Types of Cystoscopy Procedures
Two main types of cystoscopes are used: flexible or rigid.
A flexible cystoscope is a thin telescope which is passed into the bladder via the urethra; it is about as thick as a pencil. As the cystoscope is flexible, it usually passes easily along the curves of the urethra. The flexible tip can also be moved so the doctor can look at all the inside lining of the bladder and the opening of the ureters.
A rigid cystoscope is a shorter, rigid telescope. It allows a greater variety of devices to pass down side channels so that the doctor can, for example, take samples or inject into the bladder. Sometimes, it is necessary to perform a rigid cystoscopy at a later date after a flexible cystoscopy.